Tree
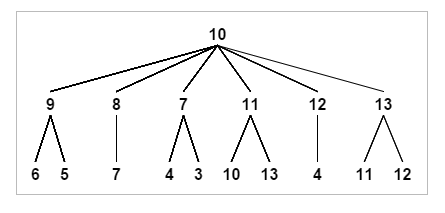
A tree is a data structure that its visualization resembles a real tree. However, we call the top of the tree as root!
In this post, we will work with a binary tree which is a subtype of tree data structure. In order to be a binary tree, which node of the tree must have up to two other nodes (one left and one right). We also can assume that which left and right site of the node are a another binary tree.
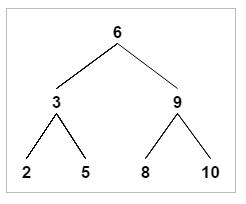
Balanced Binary Tree
That being said, let’s define what a balanced binary tree is.
According to Gayle McDowell on her book Cracking the Coding Interview, a balanced binary tree is a tree that, for each level, the difference between the depths of the subtrees should not be more than one.
So, basically, our function will call itself recursively for each node checking the depth of each subtree.
def isBalanced(self,root): # Check if root is null if root == None: return 0 # Calculate the depth of the left subtree (recursively) depthLeft = self.isBalanced(root.left) # Calculate the depth of the right subtree (recursively) depthRight = self.isBalanced(root.right) # Return is -1 (not balanced) if -1 if found in some place # during the call if depthLeft == -1 or depthRight == -1: return -1 # If the difference is greater than 1, return -1 if (depthLeft-depthRight) > 1: return -1 # Otherwise return the max depth return max(depthLeft+1,depthRight+1)
Node Class
In this example, we used a class to define a Node.
class node: # Initiate an instance of Node def __init__(self,value,left=None,right=None): self.value = value self.left = left self.right = right def __setitem__(self,index,value): self[index] = value def __getitem__(self,index): return self[index] # Print the instance's value def __str__(self): return str(self.value)
Downloads and more
You can find the raw file on Github.
Any comments or suggestions are welcome.